Last updated on March 1st, 2025 at 07:29 pm
Here, we see a Redundant Connection LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Array, Dynamic Programming
Companies
Level of Question
Medium

Redundant Connection LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
In this problem, a tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to n, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an array edges of length n where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of n nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.
Example 1:
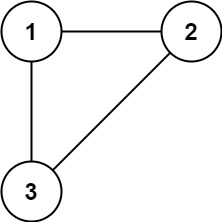
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: [2,3]
Example 2:
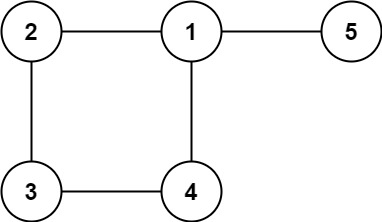
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]]
Output: [1,4]
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in this code is Union-Find (Disjoint Set Union – DSU). Union-Find is commonly used to solve problems related to connected components in a graph, such as detecting cycles, finding connected components, or determining if two nodes are in the same component.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Redundant Connection C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> parent;
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
if(edges.size()==0) return{};
parent.resize(edges.size()+1);
for(int i=1;i<edges.size()+1;i++){
parent[i]=i;
}
for(vector<int> edge : edges){
int f1=find(edge[0]);
int f2=find(edge[1]);
if(f1!=f2)
parent[f1]=f2;
else
return edge;
}
return {};
}
int find(int x){
return parent[x]==x ? x : find(parent[x]);
}
};
3.2 Redundant Connection Java
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
par = new int[edges.length+1];
for (int i = 0; i < par.length; i++)
par[i] = i;
for (int[] e : edges)
if (find(e[0]) == find(e[1])) return e;
else union(e[0],e[1]);
return edges[0];
}
private int[] par;
private int find(int x) {
if (x != par[x]) par[x] = find(par[x]);
return par[x];
}
private void union(int x, int y) {
par[find(y)] = find(x);
}
}
3.3 Redundant Connection JavaScript
var findRedundantConnection = function(edges) {
let par = Array.from({length: edges.length + 1}, (_,i) => i)
const find = x => x === par[x] ? par[x] : par[x] = find(par[x])
const union = (x,y) => par[find(y)] = find(x)
for (let [a,b] of edges)
if (find(a) === find(b)) return [a,b]
else union(a,b)
};
3.4 Redundant Connection Python
class Solution(object):
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges):
par = [i for i in range(len(edges) + 1)]
def find(x):
if x != par[x]: par[x] = find(par[x])
return par[x]
def union(x, y):
par[find(y)] = find(x)
for a,b in edges:
if find(a) == find(b): return [a,b]
else: union(a,b)
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(E * α(N)) | O(N) |
| Java | O(E * α(N)) | O(N) |
| JavaScript | O(E * α(N)) | O(N) |
| Python | O(E * α(N)) | O(N) |
here, E is the number of edges and N is the number of nodes.
- The code uses the Union-Find algorithm to detect cycles in a graph.
- The time complexity is nearly linear due to the efficient path compression in the
findoperation. - The space complexity is linear because of the parent array used to store the connected components.