Last updated on February 2nd, 2025 at 06:50 am
Here, we see the Path Sum II LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Depth-First Search, Tree
Companies
Bloomberg
Level of Question
Medium

Path Sum II LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
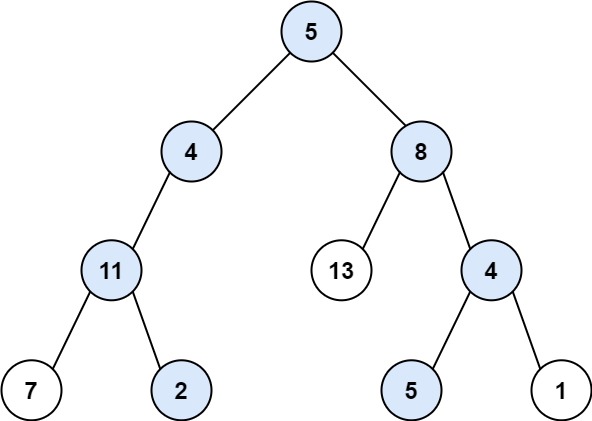
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum: 5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22 5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
Output: []
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in the provided code is Tree Depth First Search (DFS). The code traverses a binary tree using a recursive DFS approach to find all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values equals the target sum. This is a classic DFS problem where recursion is used to explore all possible paths in the tree.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Path Sum II C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int> > paths;
vector<int> path;
findPaths(root, targetSum, path, paths);
return paths;
}
private:
void findPaths(TreeNode* node, int sum, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int> >& paths) {
if (!node) return;
path.push_back(node -> val);
if (!(node -> left) && !(node -> right) && sum == node -> val)
paths.push_back(path);
findPaths(node -> left, sum - node -> val, path, paths);
findPaths(node -> right, sum - node -> val, path, paths);
path.pop_back();
}
};
3.2 Path Sum II Java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
private void dfs(TreeNode node, List<Integer> path, int remainingSum) {
if (node == null) return;
path.add(node.val);
if (node.left == null && node.right == null && remainingSum == node.val) ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
this.dfs(node.left, path, remainingSum - node.val);
this.dfs(node.right, path, remainingSum - node.val);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
dfs(root, path, targetSum);
return ans;
}
}
3.3 Path Sum II JavaScript
var pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
function dfs(node, curPath, curTarget){
if( node == null ){
return;
}
curPath.push( node.val );
curTarget -= node.val;
if( node.left == null && node.right == null && curTarget == 0 ){
answer.push( curPath.slice() );
curPath.pop();
return;
}
dfs( node.left, curPath, curTarget );
dfs( node.right, curPath, curTarget );
curPath.pop();
return;
}
answer = [];
dfs(root, [], targetSum);
return answer;
};
3.4 Path Sum II Python
class Solution:
def dfs(self, root, path, ans, remainingSum):
if not root:
return
path.append(root.val)
if not root.left and not root.right and remainingSum == root.val:
ans.append(list(path))
self.dfs(root.left, path, ans, remainingSum - root.val)
self.dfs(root.right, path, ans, remainingSum - root.val)
path.pop()
def pathSum(self, root, targetSum):
ans = []
self.dfs(root, [], ans, targetSum)
return ans
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | (O(n2)) | (O(n2)) |
| Java | (O(n2)) | (O(n2)) |
| JavaScript | (O(n2)) | (O(n2)) |
| Python | (O(n2)) | (O(n2)) |
- The code uses backtracking to explore all possible paths in the tree. Backtracking is a common technique in DFS problems.
- The space complexity is dominated by the storage of paths in the result and the recursion stack.
- The implementation is functionally equivalent across all four languages, with minor syntactic differences.