Last updated on February 28th, 2025 at 01:54 pm
Here, we see the Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Depth-First Search, Tree
Companies
Bloomberg, Facebook, Microsoft
Level of Question
Tree

Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given a binary treestruct Node { int val; Node *left; Node *right; Node *next; }
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example 1:
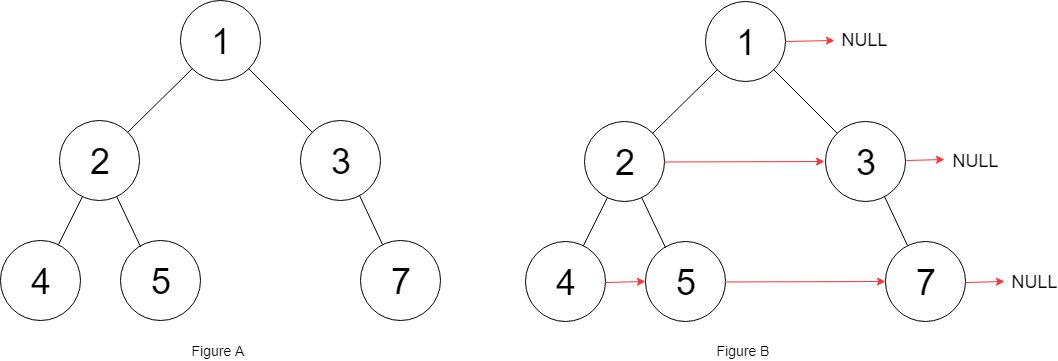
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with ‘#’ signifying the end of each level.
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in all the provided implementations is Tree Breadth-First Search (BFS). This pattern is used to traverse a tree level by level, connecting nodes at the same level. The BFS approach is evident in the Java, JavaScript, and Python implementations, where a queue is used to process nodes level by level. The C++ implementation, while not explicitly using a queue, also processes nodes level by level, making it conceptually similar to BFS.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II C++
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
Node *currParent = root, *baseChild, *currChild, *nextChild;
while (currParent) {
while (currParent->next && !currParent->left && !currParent->right) currParent = currParent->next;
currChild = baseChild = currParent->left ? currParent->left : currParent->right;
while (currChild) {
if (currParent->right && currChild != currParent->right) nextChild = currParent->right;
else {
currParent = currParent->next;
while (currParent && !currParent->left && !currParent->right) currParent = currParent->next;
nextChild = currParent ? currParent->left ? currParent->left : currParent->right : currParent;
}
currChild->next = nextChild;
currChild = nextChild;
}
currParent = baseChild;
}
return root;
}
};
3.2 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II Java
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int levelCount = queue.size();
Node prev = null;
for (int i = 0; i < levelCount; i++) {
Node curNode = queue.poll();
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = curNode;
}
prev = curNode;
if (curNode.left != null) {
queue.add(curNode.left);
}
if (curNode.right != null) {
queue.add(curNode.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
3.3 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II JavaScript
var connect = function(root) {
if (!root) return root;
let queue = [root];
let tempQueue = [];
while(queue.length){
let curr = queue.splice(0, 1)[0];
let {left, right} = curr;
if (left) tempQueue.push(left);
if (right) tempQueue.push(right);
if (queue.length === 0){
curr.next = null;
queue = tempQueue;
tempQueue = [];
}else{
curr.next = queue[0];
}
}
return root;
};
3.4 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II Python
class Solution(object):
def connect(self, root):
if not root:
return None
q = deque()
q.append(root)
dummy=Node(-999)
while q:
length=len(q)
prev=dummy
for _ in range(length):
popped=q.popleft()
if popped.left:
q.append(popped.left)
prev.next=popped.left
prev=prev.next
if popped.right:
q.append(popped.right)
prev.next=popped.right
prev=prev.next
return root
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | 1 |
| Java | O(n) | O(w) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(w) |
| Python | O(n) | O(w) |
where, N is the total number of nodes in the tree and w is the maximum width of the tree.