Last updated on March 1st, 2025 at 09:58 pm
Here, we see a Trapping Rain Water II LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Breadth-First Search, Heap
Companies
Google, Twitter
Level of Question
Hard

Trapping Rain Water II LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given an m x n integer matrix heightMap representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, return the volume of water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
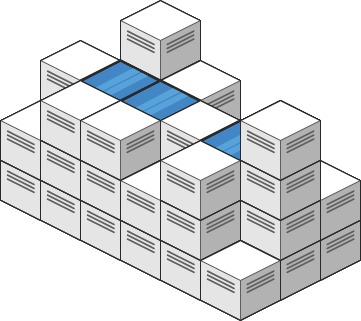
Input: heightMap = [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. We have two small ponds 1 and 3 units trapped. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
Example 2:
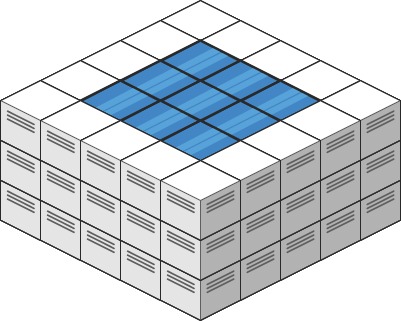
Input: heightMap = [[3,3,3,3,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,2,1,2,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,3,3,3,3]]
Output: 10
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in all the provided implementations is “Trapping Rain Water using Priority Queue (Min-Heap)”. It leverages a priority queue (min-heap) to process the boundary cells and expand inward, ensuring that the water trapped is calculated based on the minimum boundary height.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Trapping Rain Water II C++
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
int vol = 0;
const int M = heightMap.size(), N = heightMap[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited(M, vector<bool>(N, false));
vector<vector<int>> directions = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
auto comp = [&](const array<int, 3>& a, const array<int, 3>& b) { return a[0] >= b[0]; };
priority_queue<array<int, 3>, vector<array<int, 3>>, decltype(comp)> min_heap(comp);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
min_heap.push({heightMap[0][i], 0, i}),
min_heap.push({heightMap[M-1][i], M-1, i});
visited[0][i] = true, visited[M-1][i] = true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
min_heap.push({heightMap[i][0], i, 0}),
min_heap.push({heightMap[i][N-1], i, N-1});
visited[i][0] = true, visited[i][N-1] = true;
}
while(!min_heap.empty()) {
auto [height, row, col] = min_heap.top();
min_heap.pop();
for(auto dir: directions) {
int r = row + dir[0], c = col + dir[1];
if(r >= 0 && r < M && c >= 0 && c < N && !visited[r][c]) {
visited[r][c] = true;
if(heightMap[r][c] < height)
vol += height - heightMap[r][c];
min_heap.push({max(height, heightMap[r][c]), r, c});
}
}
}
return vol;
}
};
3.2 Trapping Rain Water II Java
public class Solution {
int[] dx = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = {1, -1, 0, 0};
List<int[]>[] g;
int start;
private int[] dijkstra() {
int[] dist = new int[g.length];
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2);
dist[start] = 0;
TreeSet<int[]> tree = new TreeSet<>((u, v) -> u[1] == v[1] ? u[0] - v[0] : u[1] - v[1]);
tree.add(new int[]{start, 0});
while (!tree.isEmpty()) {
int u = tree.first()[0], d = tree.pollFirst()[1];
for (int[] e : g[u]) {
int v = e[0], w = e[1];
if (Math.max(d, w) < dist[v]) {
tree.remove(new int[]{v, dist[v]});
dist[v] = Math.max(d, w);
tree.add(new int[]{v, dist[v]});
}
}
}
return dist;
}
public int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) {
if (heightMap == null || heightMap.length == 0 || heightMap[0].length == 0) return 0;
int r = heightMap.length, c = heightMap[0].length;
start = r * c;
g = new List[r * c + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
if (i == 0 || i == r - 1 || j == 0 || j == c - 1) g[start].add(new int[]{i * c + j, 0});
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if (x >= 0 && x < r && y >= 0 && y < c) g[i * c + j].add(new int[]{x * c + y, heightMap[i][j]});
}
}
int ans = 0;
int[] dist = dijkstra();
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
int cb = dist[i * c + j];
if (cb > heightMap[i][j]) ans += cb - heightMap[i][j];
}
return ans;
}
}
3.3 Trapping Rain Water II JavaScript
var trapRainWater = function (heightMap) {
if (heightMap.length < 3) return 0;
if (heightMap[0].length < 3) return 0;
let arr = new Array(heightMap.length);
let pq = new PQ();
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = new Array(heightMap[i].length).fill(false);
}
for (let i = 0; i < heightMap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < heightMap[i].length; j++) {
if (i === 0 || i === heightMap.length - 1) {
pq.push([i, j, heightMap[i][j]]);
} else if (j === 0 || j === arr[i].length - 1) {
pq.push([i, j, heightMap[i][j]]);
}
}
}
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
let [i, j, height] = pq.pop();
arr[i][j] = true;
const dir = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]];
for (let [nI, nJ] of dir) {
if ((i + nI) >= heightMap.length) continue;
if ((i + nI) < 0) continue;
if ((j + nJ) >= heightMap[i].length) continue;
if ((j + nJ) < 0) continue;
if (arr[i + nI][j + nJ]) continue;
if (heightMap[i + nI][j + nJ] < height) {
total += (height - heightMap[i + nI][j + nJ]);
heightMap[i + nI][j + nJ] = height;
}
arr[i + nI][j + nJ] = true;
pq.push([i + nI, j + nJ, heightMap[i + nI][j + nJ]])
}
}
return total;
};
class PQ {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
push(element) {
this.heap.push(element);
this.bubbleUp(this.heap.length - 1);
}
pop() {
const top = this.heap[0];
const last = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = last;
this.sinkDown(0);
}
return top;
}
peek() {
return this.heap[0];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.heap.length === 0;
}
bubbleUp(index) {
let element = this.heap[index];
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
let parent = this.heap[parentIndex];
if (element[2] >= parent[2]) break;
this.heap[parentIndex] = element;
this.heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
}
}
sinkDown(index) {
let length = this.heap.length;
let element = this.heap[index];
let elementPriority = element[2];
while (true) {
let smallestChildIndex = null;
let smallestChildPriority = Infinity;
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2;
if (leftChildIndex < length) {
let leftChild = this.heap[leftChildIndex];
let leftChildPriority = leftChild[2];
if (leftChildPriority < smallestChildPriority) {
smallestChildIndex = leftChildIndex;
smallestChildPriority = leftChildPriority;
}
}
if (rightChildIndex < length) {
let rightChild = this.heap[rightChildIndex];
let rightChildPriority = rightChild[2];
if (rightChildPriority < smallestChildPriority) {
smallestChildIndex = rightChildIndex;
smallestChildPriority = rightChildPriority;
}
}
if (smallestChildIndex === null || elementPriority < smallestChildPriority) break;
this.heap[index] = this.heap[smallestChildIndex];
this.heap[smallestChildIndex] = element;
index = smallestChildIndex;
}
}
}
3.4 Trapping Rain Water II Python
class Solution(object):
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap):
m = len(heightMap)
n = len(heightMap[0])
heights = {}
heap = []
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if r == 0 or r == m - 1 or c == 0 or c == n - 1:
h = heightMap[r][c]
heights[(r, c)] = h
heapq.heappush(heap, (h, (r, c)))
total = 0
while len(heap) > 0:
_, (r, c) = heapq.heappop(heap)
for r_o, c_o in [(r + 1, c), (r - 1, c), (r, c + 1), (r, c - 1)]:
if 0 <= r_o < m and 0 <= c_o < n and (r_o, c_o) not in heights:
h = max(heights[(r, c)], heightMap[r_o][c_o])
heights[(r_o, c_o)] = h
total += h - heightMap[r_o][c_o]
heapq.heappush(heap, (h, (r_o, c_o)))
return total
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(M * N * log(M * N)) | O(M * N) |
| Java | O(M * N * log(M * N)) | O(M * N) |
| JavaScript | O(M * N * log(M * N)) | O(M * N) |
| Python | O(M * N * log(M * N)) | O(M * N) |
- The algorithm is efficient for large grids due to the use of a priority queue, which ensures that cells are processed in the correct order of height.
- The approach is similar across all languages, with minor differences in syntax and implementation details (e.g.,
priority_queuein C++,TreeSetin Java, custom heap in JavaScript, andheapqin Python).