Last updated on March 7th, 2025 at 10:09 pm
Here, we see the Swap Nodes in Pairs LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Linked List, Recursion
Companies
Bloomberg, Microsoft, Uber
Level of Question
Medium

Swap Nodes in Pairs LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list’s nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
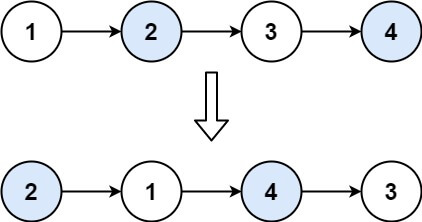
Example 1: (fig-1) Input: head = [1,2,3,4] Output: [2,1,4,3]
Example 2: Input: head = [] Output: [] Example 3: Input: head = [1] Output: [1]
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in all the provided implementations is “In-place Reversal of a LinkedList”. This pattern involves reversing or swapping nodes in a linked list without using extra space for a new list. The goal is to modify the linked list directly by rearranging the pointers.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Swap Nodes in Pairs C++
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode* temp;
temp = head->next;
head->next = swapPairs(head->next->next);
temp->next = head;
return temp;
}
};
3.2 Swap Nodes in Pairs Java
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode prevNode = new ListNode(0);
prevNode.next = head;
ListNode newHead = prevNode;
while(prevNode.next!=null && prevNode.next.next!=null){
ListNode node1 = prevNode.next;
ListNode node2 = node1.next;
ListNode nextNode = node2.next;
prevNode.next = node2;
node2.next = node1;
node1.next = nextNode;
prevNode = node1;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
3.3 Swap Nodes in Pairs JavaScript
var swapPairs = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
var v1 = head, v2 = head.next, v3 = v2.next;
v2.next = v1;
v1.next = swapPairs(v3);
return v2;
};
3.4 Swap Nodes in Pairs Python
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
pre, pre.next = self, head
while pre.next and pre.next.next:
a = pre.next
b = a.next
pre.next, b.next, a.next = b, a, b.next
pre = a
return self.next
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(n) |
| Java | O(n) | O(1) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(n) |
| Python | O(n) | O(1) |
- The recursive approach (C++ and JavaScript) is elegant but uses extra space due to the recursion stack.
- The iterative approach (Java and Python) is more space-efficient and avoids recursion overhead.
- Both approaches achieve the same time complexity of O(n).