Last updated on March 2nd, 2025 at 03:42 pm
Here, we see a Sliding Puzzle LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Array
Level of Question
Hard

Sliding Puzzle LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
On an 2 x 3 board, there are five tiles labeled from 1 to 5, and an empty square represented by 0. A move consists of choosing 0 and a 4-directionally adjacent number and swapping it.
The state of the board is solved if and only if the board is [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]].
Given the puzzle board board, return the least number of moves required so that the state of the board is solved. If it is impossible for the state of the board to be solved, return -1.
Example 1:
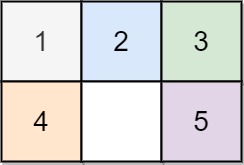
Input: board = [[1,2,3],[4,0,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: Swap the 0 and the 5 in one move.
Example 2:
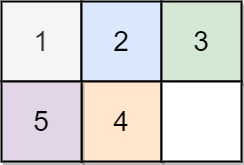
Input: board = [[1,2,3],[5,4,0]] Output: -1 Explanation: No number of moves will make the board solved.
Example 3:
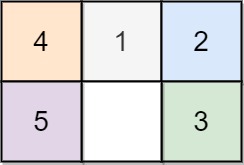
Input: board = [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]] Output: 5 Explanation: 5 is the smallest number of moves that solves the board. An example path: After move 0: [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]] After move 1: [[4,1,2],[0,5,3]] After move 2: [[0,1,2],[4,5,3]] After move 3: [[1,0,2],[4,5,3]] After move 4: [[1,2,0],[4,5,3]] After move 5: [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]]
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in all the provided implementations is Graph Breadth-First Search (BFS). This is evident because the problem involves exploring all possible states of the sliding puzzle board (represented as nodes in a graph) level by level, starting from the initial state, until the target state is reached. BFS is used to find the shortest path (minimum moves) to reach the target configuration.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Sliding Puzzle C++
class Solution {
public:
string target = "123450";
vector<vector<int>> dir{{1,3},{0,2,4},{1,5},{0,4},{1,3,5},{2,4}};
int slidingPuzzle(vector<vector<int>>& board)
{
int m = board.size(),n = board[0].size();
string first = "";
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
first += to_string(board[i][j]);
}
}
queue<pair<string,int>> q;
unordered_set<string> visited;
q.push({first,0});
visited.insert(first);
while(!q.empty())
{
int sz = q.size();
while(sz--)
{
auto cur = q.front();
q.pop();
string s = cur.first;
int count = cur.second;
if(s == target)
{
return count;
}
int indx = s.find('0');
for(auto &x: dir[indx])
{
string temp = s;
swap(temp[x],temp[indx]);
if(!visited.count(temp))
{
visited.insert(temp);
q.push({temp,count+1});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
3.2 Sliding Puzzle Java
class Solution {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int slidingPuzzle(int[][] board) {
int[] zero = {-1, -1};
outer:
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) {
zero = new int[]{i, j};
break outer;
}
}
}
helper_backtrack(board, 0, new int[]{-1, -1}, zero);
return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min;
}
public void helper_backtrack(int[][] board, int moves, int[] last, int[] curr) {
if (moves >= 20) return;
if (helper_isDone(board)) {
min = Math.min(min, moves);
return;
}
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int i = curr[0] + dir[0];
int j = curr[1] + dir[1];
if (i < 0 || i >= 2 || j < 0 || j >= 3 || (last[0] == i && last[1] == j)) continue;
int[] newMove = {i, j};
helper_flip(board, curr, newMove);
helper_backtrack(board, moves + 1, curr, newMove);
helper_flip(board, curr, newMove);
}
}
public void helper_flip(int[][] board, int[] f, int[] s) {
int temp = board[f[0]][f[1]];
board[f[0]][f[1]] = board[s[0]][s[1]];
board[s[0]][s[1]] = temp;
}
public boolean helper_isDone(int[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (i == 1 && j == 2) return true;
if (board[i][j] != 3 * i + j + 1) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
3.3 Sliding Puzzle JavaScript
var slidingPuzzle = function (board) {
const mapping = {0: [1, 3],1: [0, 2, 4], 2: [1, 5],3: [0, 4], 4: [1, 3, 5],5: [2, 4]
}
function swap(state, pos, next) {
let array = state.split('');
[array[pos], array[next]] = [array[next], array[pos]];
return array.join('');
}
let state = '';
board.forEach(row => state += row.join(''));
let visited = new Set(state);
let q = [[state, state.indexOf('0'), 0]];
while (q.length) {
let [state, pos, moves] = q.shift();
if (state == '123450')
return moves;
for (let next of mapping[pos]) {
let newState = swap(state, pos, next);
if (visited.has(newState))
continue;
visited.add(newState);
q.push([newState, next, moves + 1])
}
}
return -1;
};
3.4 Sliding Puzzle Python
class Solution(object):
def slidingPuzzle(self, board):
src = ""
zero = 0
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[i])):
src += str(board[i][j])
if board[i][j] == 0:
zero = len(src)-1
target = "123450"
step = {0:[1, 3], 1:[0, 2, 4], 2:[ 1, 5], 3:[0, 4], 4:[3, 1, 5], 5:[4, 2]}
q = collections.deque()
q.append((src, 0, zero))
visit = set()
visit.add(src)
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
arr, count, pos = q.popleft()
if arr == target:
return count
for adj_index in step[pos]:
n_arr = list(arr)
n_arr[pos], n_arr[adj_index] = n_arr[adj_index], n_arr[pos]
n_arr = "".join(n_arr)
if n_arr not in visit:
visit.add(n_arr)
q.append(( n_arr, count+1, adj_index))
return -1
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(V + E) | O(V) |
| Java | O(V + E) | O(V) |
| JavaScript | O(V + E) | O(V) |
| Python | O(V + E) | O(V) |
- BFS ensures the shortest path (minimum moves) is found.
- The recursive backtracking approach in Java is less efficient and may explore redundant states, but it still works for small inputs like the 2×3 board.
- The problem is constrained to a 2×3 board, so the number of states is small, making the algorithm feasible.