Last updated on March 1st, 2025 at 08:26 pm
Here, we see a Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Design, Tree
Companies
Amazon, Bloomberg, Facebook, Google, LinkedIn, Microsoft, Uber, Yahoo
Level of Question
Hard

Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1:
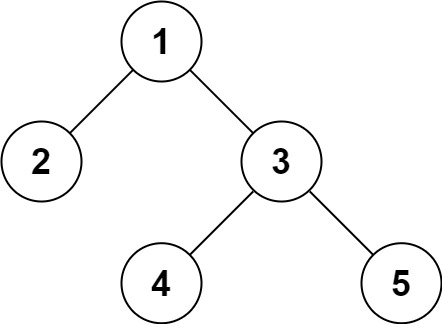
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in all the provided implementations is Tree Serialization and Deserialization. It involves converting a tree structure into a linear representation (serialization) and reconstructing the tree from the linear representation (deserialization). This pattern is commonly used in scenarios like data storage, transmission, and reconstruction of tree structures.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree C++
class Codec {
public:
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
ostringstream out;
serialize(root, out);
return out.str();
}
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream in(data);
return deserialize(in);
}
private:
void serialize(TreeNode* root, ostringstream& out) {
if (root) {
out << root->val << ' ';
serialize(root->left, out);
serialize(root->right, out);
} else {
out << "# ";
}
}
TreeNode* deserialize(istringstream& in) {
string val;
in >> val;
if (val == "#")
return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
root->left = deserialize(in);
root->right = deserialize(in);
return root;
}
};
3.2 Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree Java
public class Codec {
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return "";
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node == null) {
res.append("n ");
continue;
}
res.append(node.val + " ");
q.add(node.left);
q.add(node.right);
}
return res.toString();
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data == "") return null;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
String[] values = data.split(" ");
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
q.add(root);
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
TreeNode parent = q.poll();
if (!values[i].equals("n")) {
TreeNode left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i]));
parent.left = left;
q.add(left);
}
if (!values[++i].equals("n")) {
TreeNode right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i]));
parent.right = right;
q.add(right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
3.3 Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree JavaScript
var serialize = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return '';
}
var result = [];
var queue = [root];
while (queue.length > 0) {
var node = queue.shift();
if (node === null) {
result.push('null');
continue;
}
result.push(node.val);
queue.push(node.left);
queue.push(node.right);
}
loop: for (var i=result.length - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
if (result[i] === 'null') {
result.splice(i, 1);
}
else {
break loop;
}
}
return result.toString();
};
var deserialize = function(data) {
if (data === '') {
return null;
}
var values = data.split(',');
var root = new TreeNode(parseInt(values[0]));
var queue = [root];
for (var i=1; i < values.length; i++) {
var parent = queue.shift();
if (values[i] !== 'null') {
var left = new TreeNode(parseInt(values[i]));
parent.left = left;
queue.push(left);
}
if (values[++i] !== 'null' && i !== values.length) {
var right = new TreeNode(parseInt(values[i]));
parent.right = right;
queue.push(right);
}
}
return root;
};
3.4 Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree Python
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
def doit(node):
if node:
vals.append(str(node.val))
doit(node.left)
doit(node.right)
else:
vals.append('#')
vals = []
doit(root)
return ' '.join(vals)
def deserialize(self, data):
def doit():
val = next(vals)
if val == '#':
return None
node = TreeNode(int(val))
node.left = doit()
node.right = doit()
return node
vals = iter(data.split())
return doit()
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(n) |
| Java | O(n) | O(n) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(n) |
| Python | O(n) | O(n) |