Last updated on March 2nd, 2025 at 02:30 pm
Here, we see a Self Crossing LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Math
Level of Question
Hard

Self Crossing LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
You are given an array of integers distance.
You start at the point (0, 0) on an X-Y plane, and you move distance[0] meters to the north, then distance[1] meters to the west, distance[2] meters to the south, distance[3] meters to the east, and so on. In other words, after each move, your direction changes counter-clockwise.
Return true if your path crosses itself or false if it does not.
Example 1:
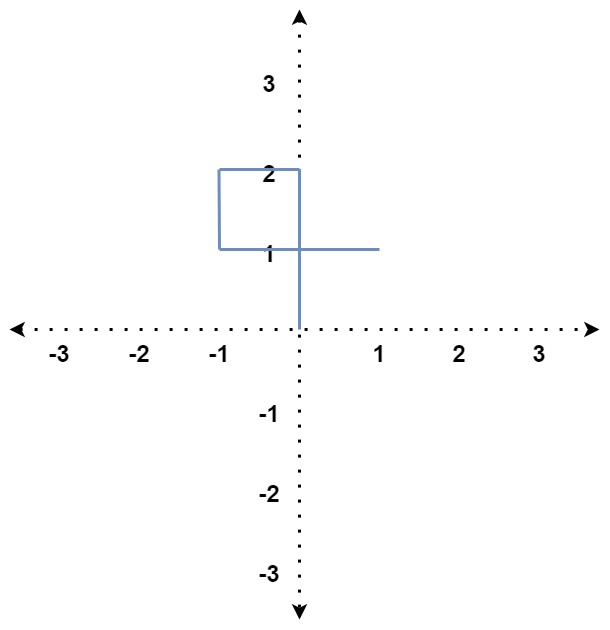
Input: distance = [2,1,1,2]
Output: true
Explanation: The path crosses itself at the point (0, 1).
Example 2:
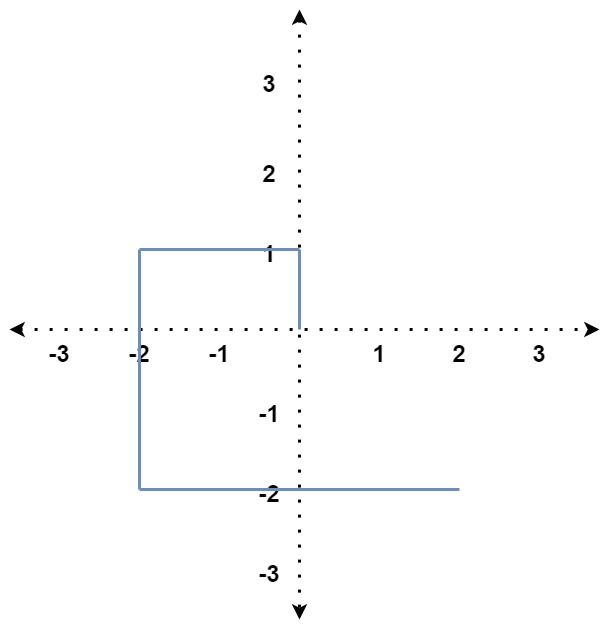
Input: distance = [1,2,3,4]
Output: false
Explanation: The path does not cross itself at any point.
Example 3:
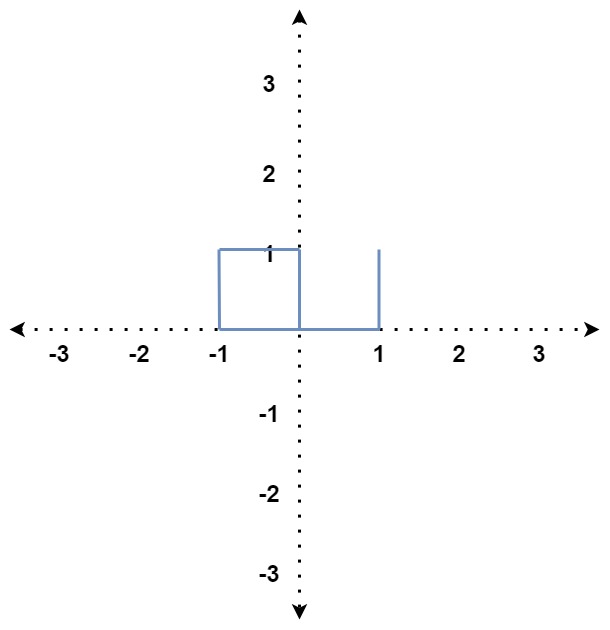
Input: distance = [1,1,1,2,1]
Output: true
Explanation: The path crosses itself at the point (0, 0).
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in this problem is Geometric Traversal. The code checks for specific geometric conditions to determine if the path formed by the distance array crosses itself.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Self Crossing C++
class Solution {
public:
bool isSelfCrossing(vector<int>& distance) {
if(distance.size()<4) return false;
distance.insert(distance.begin(),0);
for(int i=3;i<distance.size();i++){
if(distance[i]>=distance[i-2] && distance[i-1]<=distance[i-3]) return true;
if(i>=5){
if(distance[i-1]<=distance[i-3] && distance[i-2]>=distance[i-4]&& distance[i-5]>=distance[i-3]-distance[i-1] && distance[i]>=distance[i-2]-distance[i-4])
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
3.2 Self Crossing Java
class Solution {
public boolean isSelfCrossing(int[] distance) {
if (distance.length <= 3) {
return false;
}
int i = 2;
while (i < distance.length && distance[i] > distance[i - 2]) {
i++;
}
if (i >= distance.length) {
return false;
}
if ((i >= 4 && distance[i] >= distance[i - 2] - distance[i - 4]) ||
(i == 3 && distance[i] == distance[i - 2])) {
distance[i - 1] -= distance[i - 3];
}
i++;
while (i < distance.length) {
if (distance[i] >= distance[i - 2]) {
return true;
}
i++;
}
return false;
}
}
3.3 Self Crossing JavaScript
var isSelfCrossing = function (distance) {
if (distance.length <= 3) return false;
let i = 2;
while (i < distance.length && distance[i] > distance[i - 2]) i++;
if (i >= distance.length) return false;
if ((i >= 4 && distance[i] >= distance[i - 2] - distance[i - 4]) ||
(i === 3 && distance[i] === distance[i - 2])) {
distance[i - 1] -= distance[i - 3];
}
i++;
while (i < distance.length) {
if (distance[i] >= distance[i - 2]) return true;
i++;
}
return false;
};
3.4 Self Crossing Python
class Solution(object):
def isSelfCrossing(self, distance):
b = c = d = e = 0
for a in distance:
if d >= b > 0 and (a >= c or a >= c-e >= 0 and f >= d-b):
return True
b, c, d, e, f = a, b, c, d, e
return False
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(n) |
| Java | O(n) | O(1) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(1) |
| Python | O(n) | O(1) |
- The C++ implementation modifies the input array by inserting a
0at the beginning, which increases space usage. - The Java, JavaScript, and Python implementations do not modify the input array in a way that increases space complexity.
- All implementations use a single loop to traverse the array, ensuring linear time complexity.