Last updated on March 9th, 2025 at 12:10 am
Here, we see a Reverse Linked List LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Linked List
Companies
Adobe, Amazon, Apple, Bloomberg, Facebook, Microsoft, Snapchat, Twitter, Uber, Yahoo, Yelp, Zenefits
Level of Question
Easy

Reverse Linked List LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
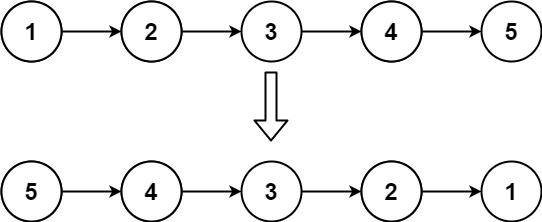
Example 1: (fig-1) Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
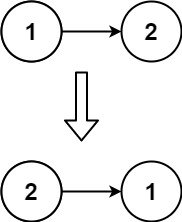
Example 2: (fig-2) Input: head = [1,2] Output: [2,1] Example 3: Input: head = [] Output: []
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in all the provided implementations is “In-place Reversal of a LinkedList”. This pattern is commonly used when reversing a linked list or performing operations that require modifying the structure of the linked list without using extra space.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Reverse Linked List C++
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *pre = new ListNode(0), *cur = head;
pre -> next = head;
while (cur && cur -> next) {
ListNode* temp = pre -> next;
pre -> next = cur -> next;
cur -> next = cur -> next -> next;
pre -> next -> next = temp;
}
return pre -> next;
}
};
3.2 Reverse Linked List Java
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null)
return head;
ListNode nextNode=head.next;
ListNode newHead=reverseList(nextNode);
nextNode.next=head;
head.next=null;
return newHead;
}
}
3.3 Reverse Linked List JavaScript
var reverseList = function(head) {
let [prev, current] = [null, head]
while(current) {
[current.next, prev, current] = [prev, current, current.next]
}
return prev
};
3.4 Reverse Linked List Python
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
prev = None
curr = head
while curr:
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
return prev
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(1) |
| Java | O(n) | O(n) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(1) |
| Python | O(n) | O(1) |