Last updated on February 4th, 2025 at 02:06 am
Here, we see a Most Frequent Subtree Sum LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Hash Table, Tree
Companies
Amazon
Level of Question
Medium

Most Frequent Subtree Sum LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the most frequent subtree sum. If there is a tie, return all the values with the highest frequency in any order.
The subtree sum of a node is defined as the sum of all the node values formed by the subtree rooted at that node (including the node itself).
Example 1:
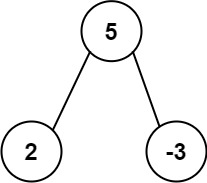
Input: root = [5,2,-3]
Output: [2,-3,4]
Example 2:
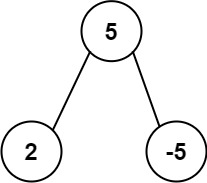
Input: root = [5,2,-5]
Output: [2]
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in this code is Tree Depth First Search (DFS). The problem involves traversing a binary tree in a post-order manner (left, right, root) to calculate the sum of all subtree nodes and track the frequency of these sums. This traversal is a classic example of DFS.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Most Frequent Subtree Sum C++
class Solution {
public:
int solve(TreeNode* root,unordered_map<int,int> &mp,int& x){
if(root ==NULL)return 0;
int l = solve(root->left,mp,x);
int r = solve(root->right,mp,x);
x = max(x,++mp[root->val+l+r]);
return root->val+l+r;
}
vector<int> findFrequentTreeSum(TreeNode* root) {
int x = -1;
unordered_map<int,int> mp;
solve(root,mp,x);
vector<int> ans;
for(auto &i: mp){
if(i.second == x){
ans.push_back(i.first);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
3.2 Most Frequent Subtree Sum Java
class Solution {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap();
int mostFreq = 0;
public int[] findFrequentTreeSum(TreeNode root) {
postorder(root);
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList();
for(int i : map.keySet()){
if(map.get(i) == mostFreq)temp.add(i);
}
int []res = new int[temp.size()];
for(int i = 0;i< temp.size();i++){
res[i] = temp.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public int postorder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null)return 0;
int left = postorder(root.left);
int right = postorder(root.right);
int sum = left + right + root.val;
map.put(sum,map.getOrDefault(sum,0) + 1);
mostFreq = Math.max(mostFreq,map.get(sum));
return sum;
}
}
3.3 Most Frequent Subtree Sum JavaScript
var findFrequentTreeSum = function(root) {
const counts = {};
const max = { val: -Infinity };
dfs(root, counts, max);
const sums = [];
for (let key in counts) {
if (counts[key] === max.val) sums.push(parseInt(key));
}
return sums;
};
function dfs(root, counts, max) {
if (!root) return 0;
let sum = root.val + dfs(root.left, counts, max) + dfs(root.right, counts, max);
counts[sum] = (counts[sum] || 0) + 1;
max.val = Math.max(max.val, counts[sum]);
return sum;
}
3.4 Most Frequent Subtree Sum Python
class Solution(object):
def findFrequentTreeSum(self, root):
freq = Counter()
def subtree_sum(node):
if not node:
return 0
s = node.val + subtree_sum(node.left) + subtree_sum(node.right)
freq[s] += 1
return s
subtree_sum(root)
max_freq = max(freq.values())
return [s for s in freq if freq[s] == max_freq]
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(n) |
| Java | O(n) | O(n) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(n) |
| Python | O(n) | O(n) |