Last updated on February 4th, 2025 at 12:47 am
Here, we see the Maximum Width of Binary Tree LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Tree
Companies
Amazon
Level of Question
Medium

Maximum Width of Binary Tree LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree.
The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes that would be present in a complete binary tree extending down to that level are also counted into the length calculation.
It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
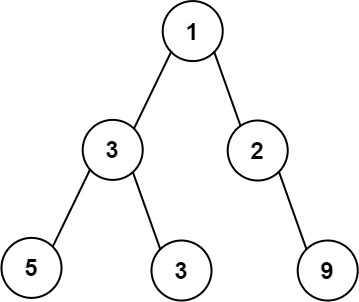
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
Output: 4
Explanation: The maximum width exists in the third level with length 4 (5,3,null,9).
Example 2:
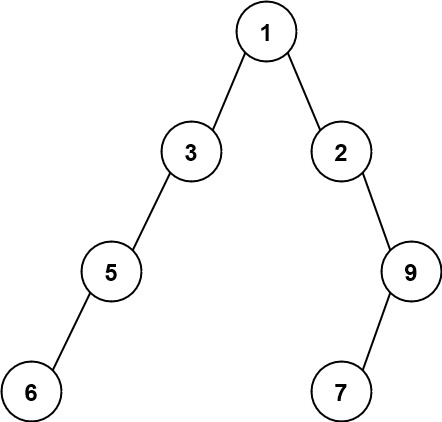
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7]
Output: 7
Explanation: The maximum width exists in the fourth level with length 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7).
Example 3:
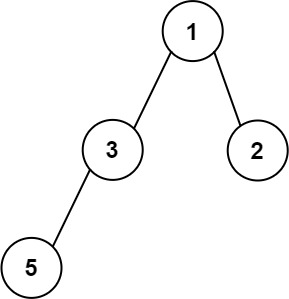
Input: root = [1,3,2,5]
Output: 2
Explanation: The maximum width exists in the second level with length 2 (3,2).
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in all the provided implementations is Tree Breadth-First Search (BFS) for the C++, Java, and Python codes, and Tree Depth-First Search (DFS) for the JavaScript code.
- Tree Breadth-First Search (BFS): The C++, Java, and Python implementations use a queue to traverse the binary tree level by level, keeping track of the indices of nodes to calculate the width of the binary tree at each level.
- Tree Depth-First Search (DFS): The JavaScript implementation uses recursion to traverse the tree depth-first, keeping track of the minimum position at each level and calculating the width of the binary tree.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Maximum Width of Binary Tree C++
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int max_width = 1;
queue<pair<TreeNode*, int>> q;
q.push({root, 0});
while (!q.empty()) {
int level_size = q.size();
int start_index = q.front().second;
int end_index = q.back().second;
max_width = max(max_width, end_index - start_index + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < level_size; ++i) {
auto node_index_pair = q.front();
TreeNode* node = node_index_pair.first;
int node_index = node_index_pair.second - start_index;
q.pop();
if (node->left != nullptr) {
q.push({node->left, 2LL * node_index + 1});
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
q.push({node->right, 2LL * node_index + 2});
}
}
}
return max_width;
}
};
3.2 Maximum Width of Binary Tree Java
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair<>(root, 0));
int maxWidth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int levelLength = queue.size();
int levelStart = queue.peek().getValue();
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < levelLength; i++) {
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> pair = queue.poll();
TreeNode node = pair.getKey();
index = pair.getValue();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(new Pair<>(node.left, 2*index));
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(new Pair<>(node.right, 2*index+1));
}
}
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, index - levelStart + 1);
}
return maxWidth;
}
}
3.3 Maximum Width of Binary Tree JavaScript
var widthOfBinaryTree = function(root) {
const minPos = [0];
let maxWidth = 0;
callDFS(root, 0, 0);
return maxWidth;
function callDFS(node, level, pos) {
if(!node) return;
if(minPos[level] === undefined) minPos.push(pos);
const diff = pos - minPos[level];
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, diff+1);
callDFS(node.left, level+1, diff*2);
callDFS(node.right, level+1, diff*2+1);
}
};
3.4 Maximum Width of Binary Tree Python
class Solution(object):
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
queue = deque([(root, 0)])
max_width = 0
while queue:
level_length = len(queue)
_, level_start = queue[0]
for i in range(level_length):
node, index = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left, 2*index))
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right, 2*index+1))
max_width = max(max_width, index - level_start + 1)
return max_width
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(n) |
| Java | O(n) | O(n) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(h) |
| Python | O(n) | O(n) |
where, H is the height of the tree.