Last updated on October 10th, 2024 at 12:49 am
Here, We see Maximal Square LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is done in many programming languages like C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc., with different approaches.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Dynamic Programming
Companies
Airbnb, Apple, Facebook
Level of Question
Medium

Maximal Square LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Given an m x n binary matrix filled with 0’s and 1’s, find the largest square containing only 1’s and return its area.
Example 1: (fig-1) Input: matrix = [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]] Output: 4
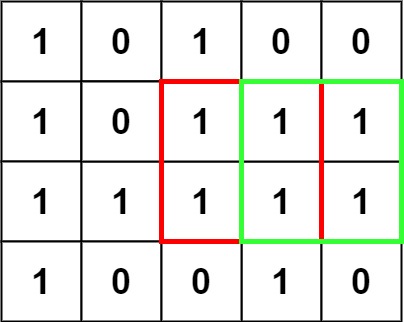
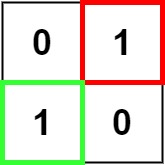
Example 2: (fig-2) Input: matrix = [["0","1"],["1","0"]] Output: 1 Example 3: Input: matrix = [["0"]] Output: 0
1. Maximal Square Leetcode Solution C++
class Solution {
public:
int maximalSquare(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.empty()) {
return 0;
}
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size(), sz = 0;
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!i || !j || matrix[i][j] == '0') {
dp[i][j] = matrix[i][j] - '0';
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])) + 1;
}
sz = max(dp[i][j], sz);
}
}
return sz * sz;
}
};1.1 Explanation
- Initialization:
- Check if the matrix is empty. If so, return 0.
- Initialize variables for the matrix dimensions (m and n) and the size of the largest square (sz).
- Create a 2D DP array dp with the same dimensions as the matrix, initialized to 0.
- DP Array Update:
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix:
- If the cell is on the border or contains ‘0’, set the DP value to the cell value.
- Otherwise, calculate the size of the square ending at that cell using the minimum value from the top, left, and top-left diagonal cells in the DP array, then add 1.
- Update sz with the maximum value in the DP array.
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix:
- Return Result:
- Return the area of the largest square (sz * sz).
1.2 Time Complexity
- O(m×n), where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns.
1.3 Space Complexity
- O(m×n) for the DP array.
2. Maximal Square Leetcode Solution Java
class Solution {
public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
return 0;
int max = 0, n = matrix.length, m = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (matrix[i - 1][j - 1] == '1') {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])) + 1;
max = Math.max(max, dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
return max * max;
}
}2.1 Explanation
- Initialization:
- Check if the matrix is null or empty. If so, return 0.
- Initialize variables for the matrix dimensions (n and m) and the size of the largest square (max).
- Create a 2D DP array dp with dimensions (n+1) x (m+1), initialized to 0.
- DP Array Update:
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix starting from (1, 1) to (n, m):
- If the cell contains ‘1’, calculate the size of the square ending at that cell using the minimum value from the top, left, and top-left diagonal cells in the DP array, then add 1.
- Update max with the maximum value in the DP array.
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix starting from (1, 1) to (n, m):
- Return Result:
- Return the area of the largest square (max * max).
2.2 Time Complexity
- O(n×m), where n is the number of rows and m is the number of columns.
2.3 Space Complexity
- O(n×m) for the DP array.
3. Maximal Square Leetcode Solution JavaScript
var maximalSquare = function(matrix) {
let max = 0
for (let i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "0") continue
if(i > 0 && j > 0)
matrix[i][j] = Math.min(matrix[i - 1][j], matrix[i][j - 1], matrix[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1
max = Math.max(matrix[i][j], max)
}
}
return max ** 2
};3.1 Explanation
- Initialization:
- Initialize the maximum size of the square (max) to 0.
- Matrix Update:
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix:
- Skip cells with ‘0’.
- If not on the border, calculate the size of the square ending at that cell using the minimum value from the top, left, and top-left diagonal cells, then add 1.
- Update max with the maximum value in the matrix.
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix:
- Return Result:
- Return the area of the largest square (max ** 2).
3.2 Time Complexity
- O(n×m), where n is the number of rows and m is the number of columns.
3.3 Space Complexity
- O(1) since the matrix itself is used for DP.
4. Maximal Square Leetcode Solution Python
class Solution(object):
def maximalSquare(self, matrix):
if matrix is None or len(matrix) < 1:
return 0
rows = len(matrix)
cols = len(matrix[0])
dp = [[0]*(cols+1) for _ in range(rows+1)]
max_side = 0
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
if matrix[r][c] == '1':
dp[r+1][c+1] = min(dp[r][c], dp[r+1][c], dp[r][c+1]) + 1 # Be careful of the indexing since dp grid has additional row and column
max_side = max(max_side, dp[r+1][c+1])
return max_side * max_side4.1 Explanation
- Initialization:
- Check if the matrix is null or empty. If so, return 0.
- Initialize variables for the number of rows (rows) and columns (cols).
- Create a 2D DP array dp with dimensions (rows+1) x (cols+1), initialized to 0.
- DP Array Update:
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix:
- If the cell contains ‘1’, calculate the size of the square ending at that cell using the minimum value from the top, left, and top-left diagonal cells in the DP array, then add 1.
- Update max_side with the maximum value in the DP array.
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix:
- Return Result:
- Return the area of the largest square (max_side * max_side).
4.2 Time Complexity
- O(n×m), where n is the number of rows and m is the number of columns.
4.3 Space Complexity
- O(n×m) for the DP array.