Last updated on February 28th, 2025 at 01:31 pm
Here, we see a Find Bottom Left Tree Value LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Breadth-First Search, Depth-First Search, Tree
Companies
Microsoft
Level of Question
Medium

Find Bottom Left Tree Value LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
Example 1:
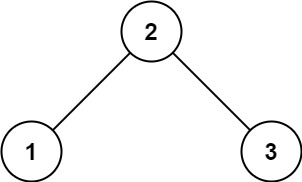
Input: root = [2,1,3]
Output: 1
Example 2:
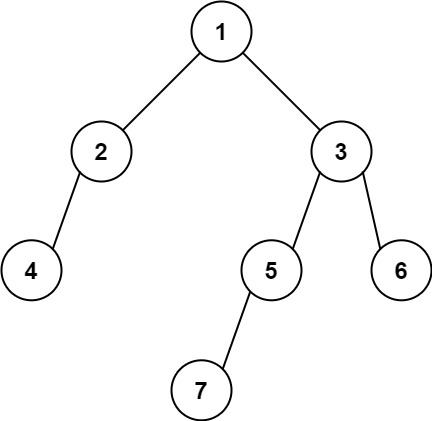
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
Output: 7
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in the provided code is Tree Breadth-First Search (BFS). This pattern involves traversing a tree level by level, typically using a queue to process nodes in the order they are encountered. In this specific problem, the BFS traversal is modified to process nodes from right to left at each level, ensuring that the last node processed is the leftmost node of the bottom-most level.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Find Bottom Left Tree Value C++
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int leftmost_value;
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
leftmost_value = node->val;
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
}
return leftmost_value;
}
};
3.2 Find Bottom Left Tree Value Java
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(q.peek() != null) {
root = q.poll();
if(root.right !=null) q.offer(root.right);
if(root.left !=null) q.offer(root.left);
}
return root.val;
}
}
3.3 Find Bottom Left Tree Value JavaScript
var findBottomLeftValue = function(root) {
const queue = [root];
let leftmostValue;
while (queue.length > 0) {
const node = queue.shift();
leftmostValue = node.val;
if (node.right) {
queue.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left) {
queue.push(node.left);
}
}
return leftmostValue;
};
3.4 Find Bottom Left Tree Value Python
class Solution(object):
def findBottomLeftValue(self, root):
queue = deque([root])
leftmost_value = None
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
leftmost_value = node.val
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
return leftmost_value
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(n) |
| Java | O(n) | O(n) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(n) |
| Python | O(n) | O(n) |
- The traversal order (right-to-left) ensures that the last node processed is the leftmost node of the bottom-most level.
- The implementation is consistent across all four languages, with minor syntactic differences.
- The BFS pattern is ideal for problems requiring level-order traversal or finding specific nodes at the deepest level of a tree.