Last updated on March 2nd, 2025 at 02:06 pm
Here, we see a Falling Squares LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Ordered Map, Segment Tree
Companies
Uber
Level of Question
Hard

Falling Squares LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
There are several squares being dropped onto the X-axis of a 2D plane.
You are given a 2D integer array positions where positions[i] = [lefti, sideLengthi] represents the ith square with a side length of sideLengthi that is dropped with its left edge aligned with X-coordinate lefti.
Each square is dropped one at a time from a height above any landed squares. It then falls downward (negative Y direction) until it either lands on the top side of another square or on the X-axis. A square brushing the left/right side of another square does not count as landing on it. Once it lands, it freezes in place and cannot be moved.
After each square is dropped, you must record the height of the current tallest stack of squares.
Return an integer array ans where ans[i] represents the height described above after dropping the ith square.
Example 1:
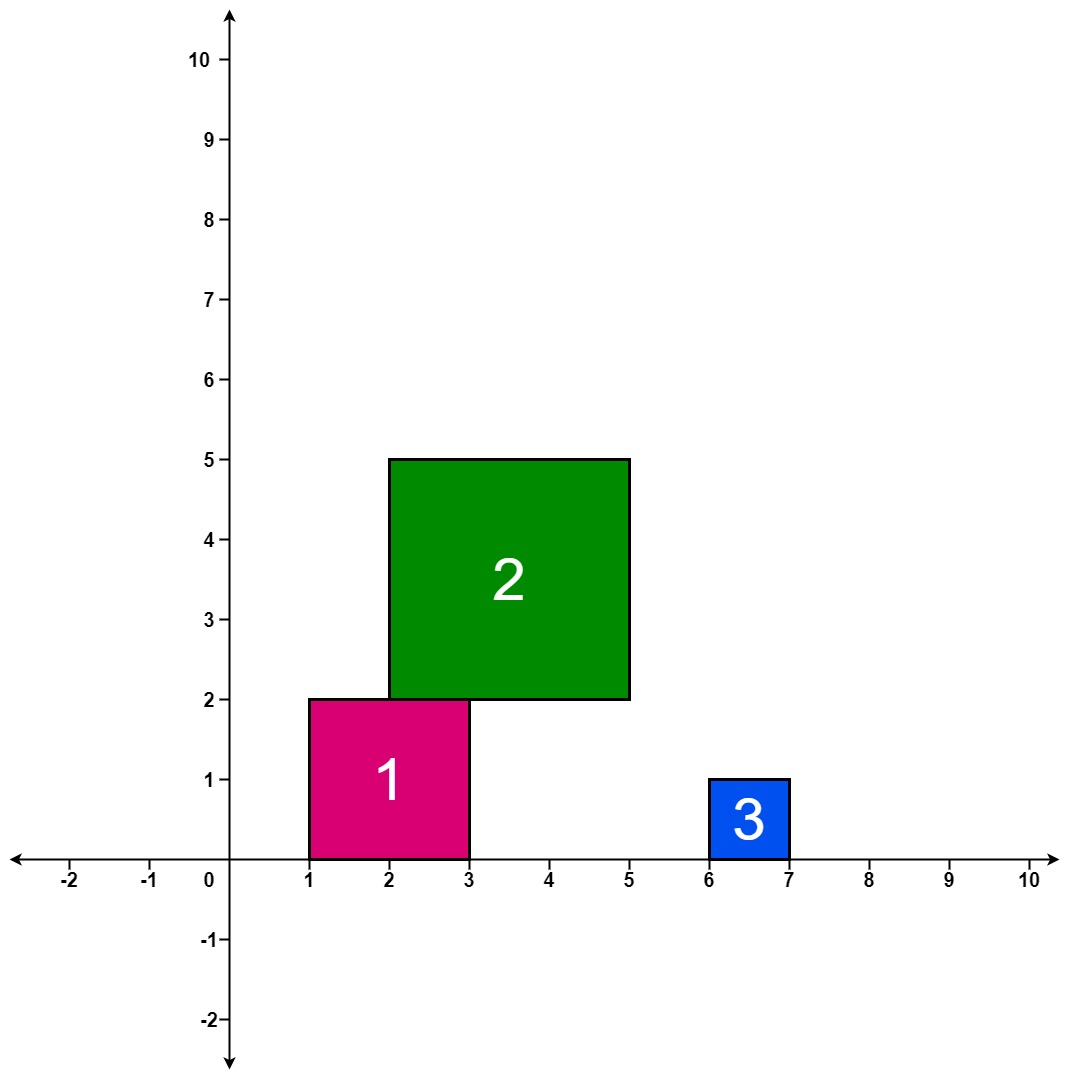
Input: positions = [[1,2],[2,3],[6,1]]
Output: [2,5,5]
Explanation: After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 2. After the second drop, the tallest stack is squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. After the third drop, the tallest stack is still squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. Thus, we return an answer of [2, 5, 5].
Example 2:
Input: positions = [[100,100],[200,100]]
Output: [100,100]
Explanation: After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 100. After the second drop, the tallest stack is either square 1 or square 2, both with heights of 100. Thus, we return an answer of [100, 100]. Note that square 2 only brushes the right side of square 1, which does not count as landing on it.
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in this problem is “Segment Tree”. Segment Trees are a data structure used for efficiently performing range queries and updates on an array, such as finding the maximum, minimum, or sum of a range of elements.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Falling Squares C++
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
struct SegmentTree {
SegmentTree(int n) : n(n) {
size = 1;
while (size < n) {
size <<= 1;
}
tree.resize(2*size);
lazy.resize(2*size);
}
void add_range(int l, int r, int h) {
l += size;
r += size;
tree[l] = max(tree[l], h);
tree[r] = max(tree[r], h);
if (l != r) {
if (!(l & 1)) {
lazy[l+1] = max(lazy[l-1], h);
}
if (r & 1) {
lazy[r-1] = max(lazy[r-1], h);
}
}
l >>= 1;
r >>= 1;
while (l != r) {
tree[l] = max(tree[2*l], tree[2*l + 1]);
tree[r] = max(tree[2*r], tree[2*r + 1]);
if (l / 2 != r / 2) {
if (!(l & 1)) {
lazy[l+1] = max(lazy[l+1], h);
}
if (r & 1) {
lazy[r-1] = max(lazy[r-1], h);
}
}
l >>= 1;
r >>= 1;
}
while (l > 0) {
tree[l] = max(tree[2*l], tree[2*l + 1]);
l >>= 1;
}
}
int max_range(int l, int r) {
l += size;
r += size;
int max_val = max(tree[l], tree[r]);
while (l / 2 != r / 2) {
if (!(l & 1)) {
max_val = max(tree[l + 1], max_val);
max_val = max(lazy[l + 1], max_val);
}
if (r & 1) {
max_val = max(tree[r - 1], max_val);
max_val = max(lazy[r - 1], max_val);
}
max_val = max(max_val, lazy[l]);
max_val = max(max_val, lazy[r]);
l >>= 1;
r >>= 1;
}
max_val = max(max_val, lazy[r]);
while (l / 2 > 0) {
max_val = max(lazy[l], max_val);
l >>= 1;
}
return max_val;
}
int global_max() {
return max_range(0, n-1);
}
int size;
int n;
vector<int> tree;
vector<int> lazy;
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> fallingSquares(vector<vector<int>>& positions) {
vector<int> points;
for (const auto& rect: positions) {
points.push_back(rect[0]);
points.push_back(rect[0] + rect[1] - 1);
}
sort(begin(points), end(points));
auto new_end = unique(begin(points), end(points));
points.resize(distance(begin(points), new_end));
SegmentTree st(points.size());
vector<int> results;
int max_height = 0;
for (const auto& rect: positions) {
int x_1 = rect[0];
int x_2 = rect[0] + rect[1] - 1;
int l = distance(begin(points), lower_bound(begin(points), end(points), x_1));
int r = distance(begin(points), lower_bound(begin(points), end(points), x_2));
int cur_height = st.max_range(l, r);
int new_height = rect[1] + cur_height;
max_height = max(new_height, max_height);
st.add_range(l, r, new_height);
results.push_back(max_height);
}
return results;
}
};
3.2 Falling Squares Java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> fallingSquares(int[][] positions) {
SegmentNode root = new SegmentNode(0,Integer.MAX_VALUE,0);
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int max = 0;
for(int[] p : positions){
int left = p[0], height = p[1], right = left + height;
int maxHeight = query(root, left, right) + height;
max = Math.max(max,maxHeight);
ans.add(max);
add(root, left, right, maxHeight);
}
return ans;
}
public int query(SegmentNode root, int start, int end){
if(start<=root.start && end>=root.end) return root.maxHeight;
if(start>=root.end || end<=root.start) return 0;
if (root.left==null) return root.maxHeight;
int mid = root.start + (root.end - root.start) / 2;
if (end <= mid) {
return query(root.left, start, end);
} else if (start >= mid) {
return query(root.right, start, end);
}
return Math.max(query(root.left,start,mid),query(root.right,mid,end));
}
public void add(SegmentNode root, int start, int end, int maxHeight){
if(start<=root.start && end>=root.end){
root.maxHeight = maxHeight;
root.left = null;
root.right = null;
return;
}
if(start>=root.end || root.start>=end) return;
if(root.left==null){
int mid = root.start + (root.end - root.start) / 2;
root.left = new SegmentNode(root.start,mid,0);
root.right = new SegmentNode(mid,root.end,0);
}
add(root.left,start,end,maxHeight);
add(root.right,start,end,maxHeight);
root.maxHeight = Math.max(root.left.maxHeight,root.right.maxHeight);
}
}
class SegmentNode{
public SegmentNode left , right;
public int start, end, maxHeight;
public SegmentNode(int start, int end, int maxHeight){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.maxHeight = maxHeight;
}
}
3.3 Falling Squares JavaScript
var fallingSquares = function (positions) {
let height = [];
let squares = [[0, 1e10, 0]];
for (let p of positions) {
for (let i = 0; i < squares.length; ++i) {
let l = squares[i][0];
let r = squares[i][1] + l;
if (p[0] < r && ((p[0] + p[1]) > l)) {
let square = [...p, p[1] + squares[i][2]];
for (let j = 0; j < i + 1; ++j) {
if (squares[j][2] < square[2]) {
squares.splice(j, 0, square);
break;
}
}
height.push(squares[0][2]);
break;
}
}
}
return height;
};
3.4 Falling Squares Python
class Solution(object):
def fallingSquares(self, positions):
heights, result = [], []
highest = 0
for i, position in enumerate(positions):
left, side_length = position[0], position[1]
base_height = 0
for j in range(i):
prev_left, prev_side = positions[j][0], positions[j][1]
if (left + side_length <= prev_left) or (left >= prev_left + prev_side):
continue
base_height = max(base_height, heights[j])
heights.append(base_height + side_length)
highest = max(highest, heights[-1])
result.append(highest)
return result
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n log n) | O(n) |
| Java | O(n log n) | O(n) |
| JavaScript | O(n2) | O(n) |
| Python | O(n2) | O(n) |
- C++ and Java use a Segment Tree, which is efficient for range queries and updates, resulting in O(n log n) time complexity.
- JavaScript and Python use simpler approaches (interval list and brute force, respectively), leading to O(n2) time complexity.
- All implementations use O(n) space, as they need to store information about the squares or intervals.