Last updated on February 20th, 2025 at 09:52 am
Here, we see an Employee Importance LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Breadth First Search, Depth First Search, Hash Table
Companies
Uber
Level of Question
Medium

Employee Importance LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
You have a data structure of employee information, including the employee’s unique ID, importance value, and direct subordinates’ IDs.
You are given an array of employees employees where:
- employees[i].id is the ID of the ith employee.
- employees[i].importance is the importance value of the ith employee.
- employees[i].subordinates is a list of the IDs of the direct subordinates of the ith employee.
Given an integer id that represents an employee’s ID, return the total importance value of this employee and all their direct and indirect subordinates.
Example 1:
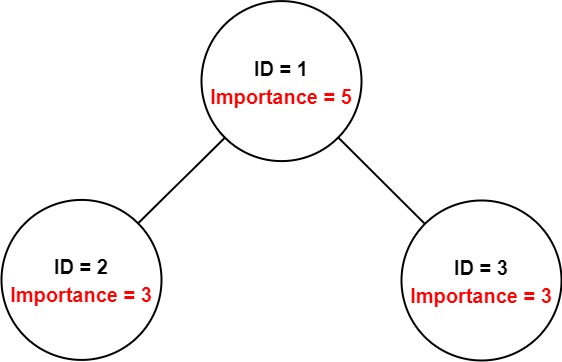
Input: employees = [[1,5,[2,3]],[2,3,[]],[3,3,[]]], id = 1
Output: 11
Explanation: Employee 1 has an importance value of 5 and has two direct subordinates: employee 2 and employee 3. They both have an importance value of 3. Thus, the total importance value of employee 1 is 5 + 3 + 3 = 11.
Example 2:
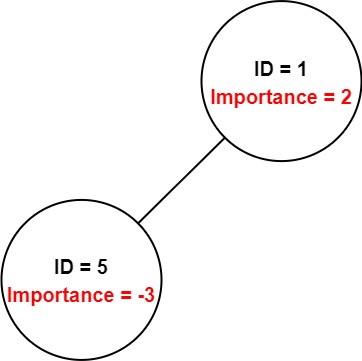
Input: employees = [[1,2,[5]],[5,-3,[]]], id = 5
Output: -3
Explanation: Employee 5 has an importance value of -3 and has no direct subordinates. Thus, the total importance value of employee 5 is -3.
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in the provided code is Graph Traversal. Specifically:
- The C++ and JavaScript implementations use Breadth-First Search (BFS).
- The Java and Python implementations use Depth-First Search (DFS).
This problem can be thought of as traversing a graph where each employee is a node, and their subordinates are the edges. The goal is to calculate the total “importance” of the given employee and all their subordinates.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Employee Importance C++
class Solution {
public:
int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {
unordered_map<int, Employee*>m;
for(auto x: employees) m[x->id] = x;
int sum = 0;
deque<Employee*>q;
q.push_back(m[id]);
while(!q.empty()){
auto p = q.front();
q.pop_front();
for(auto x: p->subordinates) q.push_back(m[x]);
sum += p->importance;
}
return sum;
}
};
3.2 Employee Importance Java
class Solution {
public int getImportance(List<Employee> employees, int id) {
Map<Integer, Employee> inputMap = new HashMap<>();
for(Employee e : employees) {
inputMap.put(e.id, e);
}
return helper(inputMap, id);
}
private static int helper(Map<Integer, Employee> inputMap, int id) {
int imp = inputMap.get(id).importance;
for(int subId : inputMap.get(id).subordinates) {
imp += helper(inputMap, subId);
}
return imp;
}
}
3.3 Employee Importance JavaScript
var GetImportance = function(employees, id) {
let employeeMap = new Map();
for (employee of employees) {
employeeMap.set(employee.id, {importance : employee.importance, sub : employee.subordinates})
}
let totalImportance = 0;
let queue = [id];
while(queue.length > 0) {
let currentEmployee = employeeMap.get(queue.shift());
totalImportance += currentEmployee.importance;
queue.push(...currentEmployee.sub)
}
return totalImportance
};
3.4 Employee Importance Python
class Solution(object):
def getImportance(self, employees, id):
def dfs(emp):
imp = emps[emp].importance
for s in emps[emp].subordinates:
imp += dfs(s)
return imp
emps= {emp.id: emp for emp in employees}
return dfs(id)
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(N) | O(N) |
| Java | O(N) | O(N) |
| JavaScript | O(N) | O(N) |
| Python | O(N) | O(N) |
- Time Complexity: The traversal ensures that each employee is visited exactly once, making the time complexity O(N), where N is the number of employees.
- Space Complexity: The space complexity is O(N) due to the storage of the employee map and the queue (BFS) or recursion stack (DFS).
- Coding Pattern: The problem is a Graph Traversal problem, with BFS and DFS being the two approaches used in the implementations.