Last updated on March 1st, 2025 at 09:26 pm
Here, we see a Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Depth-First Search, Tree
Companies
Baidu, Microsoft
Level of Question
Hard

Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node’s values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1:
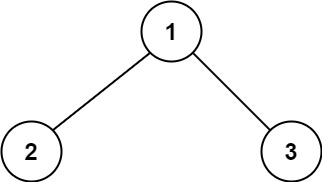
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
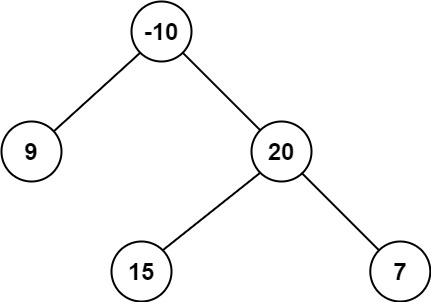
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in the provided code is “Tree Depth First Search (DFS)”. The code traverses the binary tree using a recursive DFS approach to calculate the maximum path sum. This pattern is commonly used when solving problems that require exploring all possible paths in a tree structure.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
int maxPath = INT_MIN;
DFS(root, maxPath);
return maxPath;
}
private:
int DFS(TreeNode* root, int& maxPath) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0; // Base case: return 0 if the node is NULL
}
int lmax = max(DFS(root->left, maxPath), 0);
int rmax = max(DFS(root->right, maxPath), 0);
maxPath = max(maxPath, root->val + lmax + rmax);
return root->val + max(lmax, rmax);
}
};
3.2 Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum Java
class Solution {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPath(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int value = root.val;
int left_sum = Math.max(maxPath(root.left),0);
int right_sum = Math.max(maxPath(root.right),0);
max = Math.max(max, left_sum + right_sum + value);
return Math.max(left_sum, right_sum) + value;
}
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
maxPath(root);
return max;
}
}
3.3 Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum JavaScript
var maxPathSum = function (root) {
const ans = { val: -Infinity };
dfs(root, ans);
return ans.val;
};
function dfs(root, ans) {
if (!root) return 0;
const left = dfs(root.left, ans);
const right = dfs(root.right, ans);
const maxVal = Math.max(root.val, root.val + left, root.val + right);
ans.val = Math.max(ans.val, maxVal, root.val + left + right);
return maxVal;
}
3.4 Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum Python
class Solution(object):
def maxPathSum(self, root):
ans = [root.val]
def DFS(root):
if root == None:
return 0
lmax = max(0, DFS(root.left))
rmax = max(0, DFS(root.right))
ans[0] = max(ans[0] , root.val + lmax + rmax)
return root.val + max(lmax , rmax)
DFS(root)
return ans[0]
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(n) | O(h) |
| Java | O(n) | O(h) |
| JavaScript | O(n) | O(h) |
| Python | O(n) | O(h) |
where H is the height of the tree.