Last updated on February 2nd, 2025 at 05:16 am
Here, we see the Pacific Atlantic Water Flow LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Breadth-First Search, Depth-First Search
Companies
Level of Question
Medium

Pacific Atlantic Water Flow LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
There is an m x n rectangular island that borders both the Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean touches the island’s left and top edges, and the Atlantic Ocean touches the island’s right and bottom edges.
The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. You are given an m x n integer matrix heights where heights[r][c] represents the height above sea level of the cell at coordinate (r, c).
The island receives a lot of rain, and the rain water can flow to neighboring cells directly north, south, east, and west if the neighboring cell’s height is less than or equal to the current cell’s height. Water can flow from any cell adjacent to an ocean into the ocean.
Return a 2D list of grid coordinates result where result[i] = [ri, ci] denotes that rain water can flow from cell (ri, ci) to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 1:
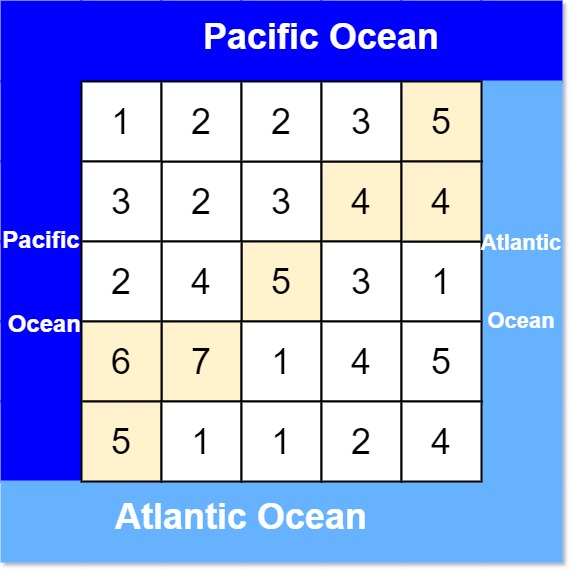
Input: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
Output: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
Explanation: The following cells can flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, as shown below:
[0,4]: [0,4] -> Pacific Ocean
[0,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[1,3]: [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean
[1,3] -> [1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[1,4]: [1,4] -> [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean
[1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[2,2]: [2,2] -> [1,2] -> [0,2] -> Pacific Ocean
[2,2] -> [2,3] -> [2,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[3,0]: [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[3,0] -> [4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean
[3,1]: [3,1] -> [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[3,1] -> [4,1] -> Atlantic Ocean
[4,0]: [4,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean Note that there are other possible paths for these cells to flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 2:
Input: heights = [[1]]
Output: [[0,0]]
Explanation: The water can flow from the only cell to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in this code is “Islands”. This pattern is commonly used to solve problems where you need to traverse a grid or matrix to find connected components or regions that satisfy certain conditions. In this case, the problem involves finding cells in a grid that can flow water to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, which is conceptually similar to finding connected regions in a grid.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 Pacific Atlantic Water Flow C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
vector<vector<int>>ans;
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(m, vector<bool>(n));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(m, vector<bool>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, n-1);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atlantic, m-1, j);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j])
ans.push_back({i,j});
}
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& h, vector<vector<bool>>& vis, int i, int j) {
int m = h.size();
int n = h[0].size();
vis[i][j] = true;
if (i-1 >= 0 && vis[i-1][j] != true && h[i-1][j] >= h[i][j])
dfs(h, vis, i-1, j);
if (i+1 < m && vis[i+1][j] != true && h[i+1][j] >= h[i][j])
dfs(h, vis, i+1, j);
if (j-1 >= 0 && vis[i][j-1] != true && h[i][j-1] >= h[i][j])
dfs(h, vis, i, j-1);
if (j+1 < n && vis[i][j+1] != true && h[i][j+1] >= h[i][j])
dfs(h, vis, i, j+1);
}
};
3.2 Pacific Atlantic Water Flow Java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int rows = heights.length, cols = heights[0].length;
boolean[][] pac = new boolean[rows][cols];
boolean[][] atl = new boolean[rows][cols];
for (int col = 0; col< cols; col++){
dfs(0, col, rows, cols, pac, heights[0][col], heights);
dfs(rows-1, col,rows, cols, atl, heights[rows-1][col], heights);
}
for (int row = 0; row<rows; row++){
dfs(row, 0,rows, cols, pac, heights[row][0], heights);
dfs(row, cols-1,rows, cols, atl, heights[row][cols-1], heights);
}
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++){
if (pac[i][j] && atl[i][j])
result.add(Arrays.asList(i,j));
}
return result;
}
private void dfs(int row, int col, int rows, int cols, boolean[][] visited, int prevHeight, int[][] heights){
if (row < 0 || row >= rows || col < 0 || col >= cols || visited[row][col] || prevHeight > heights[row][col])
return;
visited[row][col]= true;
dfs(row+1, col, rows, cols, visited, heights[row][col], heights);
dfs(row-1, col, rows, cols, visited, heights[row][col], heights);
dfs(row, col+1, rows, cols, visited, heights[row][col], heights);
dfs(row, col-1, rows, cols, visited, heights[row][col], heights);
}
}
3.3 Pacific Atlantic Water Flow JavaScript
var pacificAtlantic = function(heights) {
if (!heights.length) return heights
let y = heights.length, x = heights[0].length, ans = [],
dp = new Uint8Array(x * y)
const dfs = (i, j, w, h) => {
let ij = i * x + j
if ((dp[ij] & w) || heights[i][j] < h) return
dp[ij] += w, h = heights[i][j]
if (dp[ij] === 3) ans.push([i,j])
if (i + 1 < y) dfs(i+1, j, w, h)
if (i > 0) dfs(i-1, j, w, h)
if (j + 1 < x) dfs(i, j+1, w, h)
if (j > 0) dfs(i, j-1, w, h)
}
for (let i = 0; i < y; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, 1, heights[i][0])
dfs(i, x-1, 2, heights[i][x-1])
}
for (let j = 0; j < x; j++) {
dfs(0, j, 1, heights[0][j])
dfs(y-1, j, 2, heights[y-1][j])
}
return ans
};
3.4 Pacific Atlantic Water Flow Python
class Solution(object):
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights):
if not heights: return heights
x, y = len(heights[0]), len(heights)
ans, dp = [], [0] * (x * y)
def dfs(i, j, w, h):
ij = i * x + j
if dp[ij] & w or heights[i][j] < h: return
dp[ij] += w
h = heights[i][j]
if dp[ij] == 3: ans.append([i,j])
if i + 1 < y: dfs(i+1, j, w, h)
if i > 0: dfs(i-1, j, w, h)
if j + 1 < x: dfs(i, j+1, w, h)
if j > 0: dfs(i, j-1, w, h)
for i in range(y):
dfs(i, 0, 1, heights[i][0])
dfs(i, x-1, 2, heights[i][x-1])
for j in range(x):
dfs(0, j, 1, heights[0][j])
dfs(y-1, j, 2, heights[y-1][j])
return ans
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(M * N) | O(M * N) |
| Java | O(M * N) | O(M * N) |
| JavaScript | O(M * N) | O(M * N) |
| Python | O(M * N) | O(M * N) |