Last updated on February 20th, 2025 at 08:35 am
Here, we see a 01 Matrix LeetCode Solution. This Leetcode problem is solved using different approaches in many programming languages, such as C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, etc.
List of all LeetCode Solution
Topics
Tree
Companies
Facebook, Google
Level of Question
Medium

01 Matrix LeetCode Solution
Table of Contents
1. Problem Statement
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell. The distance between two adjacent cells is 1.
Example 1:
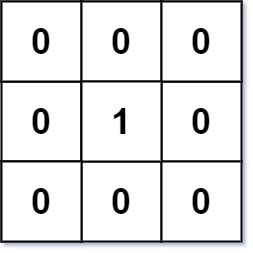
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Example 2:
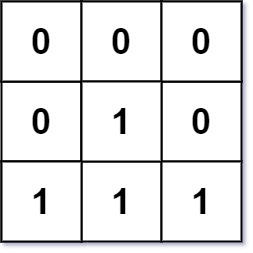
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]
2. Coding Pattern Used in Solution
The coding pattern used in this code is “Matrix Breadth-First Search (BFS)”. This pattern is commonly used to traverse a grid or matrix level by level, starting from a set of initial points (in this case, all cells with value 0) and expanding outward to update neighboring cells.
However, since this problem involves a 2D grid rather than a tree, it is more appropriate to classify it as Matrix BFS.
3. Code Implementation in Different Languages
3.1 01 Matrix C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int rows = mat.size();
int cols = mat[0].size();
vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
q.push({i, j});
} else {
mat[i][j] = INT_MAX;
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> cell = q.front();
q.pop();
int row = cell.first;
int col = cell.second;
for (pair<int, int> direction : directions) {
int newRow = row + direction.first;
int newCol = col + direction.second;
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newCol >= 0 && newCol < cols && mat[newRow][newCol] > mat[row][col] + 1) {
mat[newRow][newCol] = mat[row][col] + 1;
q.push({newRow, newCol});
}
}
}
return mat;
}
};
3.2 01 Matrix Java
class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int rows = mat.length;
int cols = mat[0].length;
int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
} else {
mat[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = queue.poll();
int row = cell[0];
int col = cell[1];
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int newRow = row + direction[0];
int newCol = col + direction[1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newCol >= 0 && newCol < cols && mat[newRow][newCol] > mat[row][col] + 1) {
mat[newRow][newCol] = mat[row][col] + 1;
queue.add(new int[]{newRow, newCol});
}
}
}
return mat;
}
}
3.3 01 Matrix JavaScript
var updateMatrix = function(mat) {
const rows = mat.length;
const cols = mat[0].length;
const directions = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]];
const queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] === 0) {
queue.push([i, j]);
} else {
mat[i][j] = Infinity;
}
}
}
while (queue.length > 0) {
const [row, col] = queue.shift();
for (const [dr, dc] of directions) {
const new_row = row + dr;
const new_col = col + dc;
if (new_row >= 0 && new_row < rows && new_col >= 0 && new_col < cols && mat[new_row][new_col] > mat[row][col] + 1) {
mat[new_row][new_col] = mat[row][col] + 1;
queue.push([new_row, new_col]);
}
}
}
return mat;
};
3.4 01 Matrix Python
class Solution(object):
def updateMatrix(self, mat):
rows, cols = len(mat), len(mat[0])
directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
queue = deque()
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if mat[i][j] == 0:
queue.append((i, j))
else:
mat[i][j] = float('inf')
while queue:
row, col = queue.popleft()
for dr, dc in directions:
new_row, new_col = row + dr, col + dc
if 0 <= new_row < rows and 0 <= new_col < cols and mat[new_row][new_col] > mat[row][col] + 1:
mat[new_row][new_col] = mat[row][col] + 1
queue.append((new_row, new_col))
return mat
4. Time and Space Complexity
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
| C++ | O(m * n) | O(m * n) |
| Java | O(m * n) | O(m * n) |
| JavaScript | O(m * n) | O(m * n) |
| Python | O(m * n) | O(m * n) |
- The code uses the Matrix BFS pattern to calculate the shortest distance from each cell to the nearest
0. - It initializes the matrix and queue, then performs a BFS traversal to update distances.
- The time complexity is O(m * n), and the space complexity is also O(m * n) for all implementations.